Our Blogs
Empowering Healthcare Professions Globally
Hypertension: The Silent Killer
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is one of the most prevalent chronic conditions worldwide. The major concerning part of hypertension is that often it presents no visible symptoms till it has progressed to the critical stage, thus dubbed, “the silent killer”.
Understanding hypertension, its secondary ailments, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention.
What is Hypertension?
Hypertension occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high. It is classified into two categories:
- Primary (Essential) Hypertension: Develops over time without a specific cause.
- Secondary Hypertension: Results from underlying conditions such as kidney disease, hormonal disorders, or medication side effects.
A blood pressure reading consistently above 140/90 mmHg is considered hypertensive, with 120/80 mmHg being the normal range.
| Category | Systolic (mmHg) | Diastolic (mmHg) |
| Normal | <120 | <80 |
| Prehypertension | 120-139 | 80-89 |
| Stages of Hypertension | ||
| Stage-1 | 140-159 | 90-99 |
| Stage-2 | >160 | >100 |
Secondary Ailments Associated with Hypertension
Hypertension rarely exists in isolation. Over time, it can lead to or exacerbate several severe health conditions:
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Prolonged high blood pressure strains the heart, leading to heart attacks, heart failure, and left ventricular hypertrophy.
- It is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease.
- Stroke
- Hypertension can cause damage to the blood vessels in the brain, increasing the risk of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
- Kidney Damage
- High blood pressure damages the arteries leading to the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste efficiently and leading to chronic kidney disease.
- Aneurysms
- Persistent hypertension weakens blood vessels, potentially causing aneurysms, which are life-threatening if ruptured.
- Eye Damage (Hypertensive Retinopathy)
- High blood pressure can damage the small blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision loss if untreated.
- Cognitive Decline
- Hypertension is linked to dementia and cognitive impairments due to reduced blood flow to the brain.
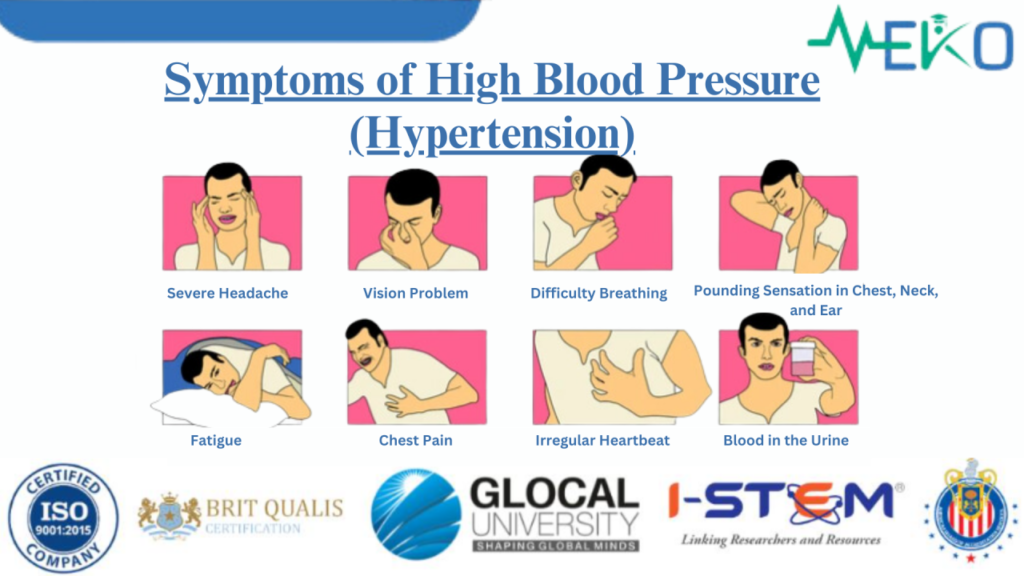
Symptoms of Hypertension
Hypertension is often asymptomatic in its early stages, but severe or prolonged cases can present with:
- Persistent headaches
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Nosebleeds (in extreme cases)
Diagnosis of Hypertension
- Regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial for diagnosis.
- Confirming high blood pressure requires consistent readings over multiple visits or ambulatory monitoring.
- Additional tests, such as blood tests, urinalysis, or imaging, may identify underlying causes or complications.
Treatment and Management
Managing hypertension effectively involves lifestyle changes, medication, or a combination of both:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Changes:
- Adopt the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy.
- Limit salt intake to less than 2,300 mg per day.
- Regular Exercise:
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly.
- Weight Management:
- Reducing even 5–10% of body weight significantly lowers blood pressure.
- Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking:
- Excessive alcohol raises blood pressure, while smoking damages blood vessels.
- Stress Reduction:
- Practices like meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises help manage stress.
Treatment and Management
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Healthy Diet: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-sodium foods.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly.
- Stress Management: Practices like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help.
- Medications:
Doctors may prescribe:- Diuretics
- ACE inhibitors
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Monitoring:
Regular blood pressure checks are vital for early detection and control.
Why Addressing Hypertension is Critical
Given its strong link to severe health complications, understanding and managing hypertension is essential for long-term wellness.
